Quiz 1-1 points lines and planes – Embarking on a journey of geometric exploration, we delve into the realm of quiz 1-1: points, lines, and planes. These fundamental concepts form the cornerstone of geometry and its myriad applications across diverse disciplines.
In this comprehensive overview, we will meticulously define and examine the properties of points, lines, and planes. We will explore their intersections and delve into their practical applications in fields such as geometry, engineering, architecture, and physics.
Points, Lines, and Planes
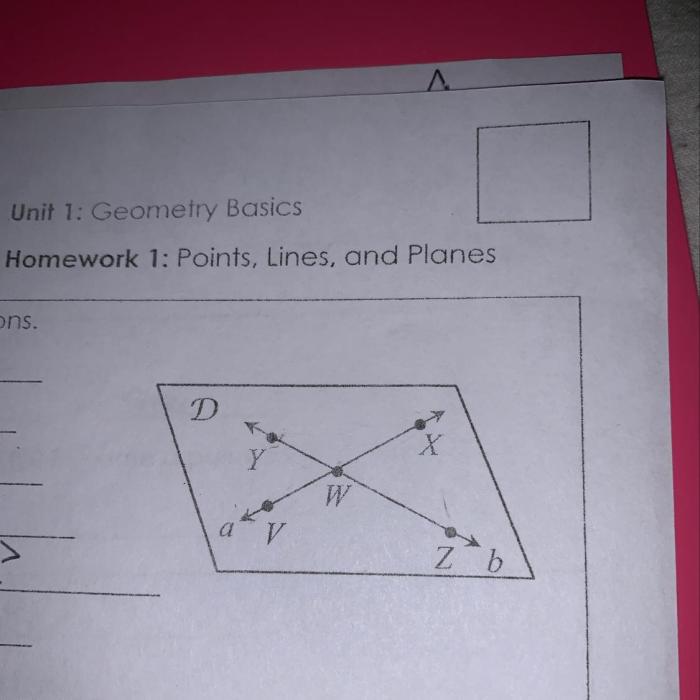
In geometry, points, lines, and planes are fundamental concepts that form the building blocks of more complex geometric shapes and structures. Understanding these basic elements is crucial for comprehending the language of geometry and its applications in various fields.
Points
A point is a geometric object that has no dimensions (length, width, or height). It is often represented by a small dot or symbol and is used to mark a specific location in space.
- Points can be used to represent the vertices of geometric shapes, such as triangles, squares, and circles.
- In physics, points can represent the location of particles or objects.
- In computer graphics, points are used to define the coordinates of pixels on a screen.
Lines
A line is a one-dimensional geometric object that extends infinitely in both directions. It is defined by two distinct points, called its endpoints, and is represented by a straight or curved path connecting them.
- Lines can be classified as straight lines (having no curvature) or curved lines (having a non-zero curvature).
- Parallel lines are lines that never intersect, while perpendicular lines intersect at right angles (90 degrees).
- Lines are used in various fields, such as engineering, architecture, and computer graphics, to represent edges, boundaries, and paths.
Planes
A plane is a two-dimensional geometric object that extends infinitely in all directions. It is defined by three non-collinear points, meaning they do not lie on the same straight line, and is represented by a flat or curved surface.
- Planes can be classified as flat planes (having no curvature) or curved planes (having a non-zero curvature).
- Planes are used in various fields, such as geometry, architecture, and engineering, to represent surfaces, walls, and roofs.
Intersections of Lines and Planes, Quiz 1-1 points lines and planes
When a line and a plane intersect, they can form different types of intersections:
- Point of intersection: A single point where the line and plane meet.
- Line of intersection: A straight line that lies in both the plane and the line.
These intersections are important in various applications, such as determining the points of contact between objects or finding the intersection of two surfaces.
Applications of Points, Lines, and Planes
Points, lines, and planes have numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Geometry: Defining geometric shapes and their properties.
- Engineering: Designing structures, bridges, and machines.
- Architecture: Creating blueprints and designing buildings.
- Physics: Representing the location of particles and objects.
- Computer graphics: Creating 3D models and animations.
FAQ Insights: Quiz 1-1 Points Lines And Planes
What is the definition of a point?
A point is a geometric object with no dimension or size. It is often represented by a dot or a small circle.
What is the difference between a straight line and a curved line?
A straight line is a line that extends infinitely in both directions without changing direction. A curved line is a line that changes direction at least once.
What is the intersection of a line and a plane?
The intersection of a line and a plane is a point.