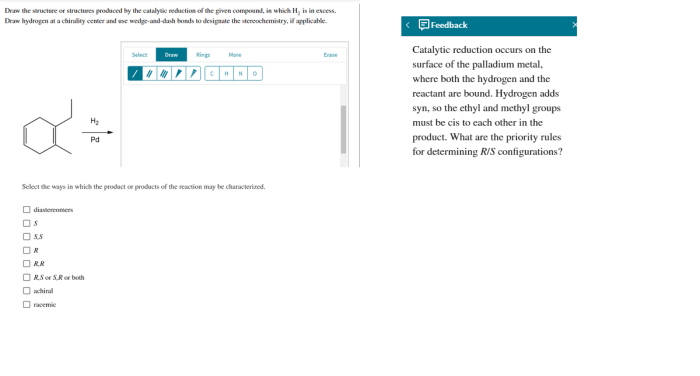
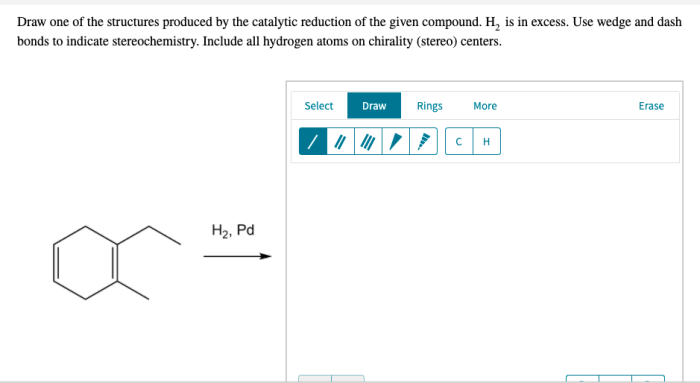
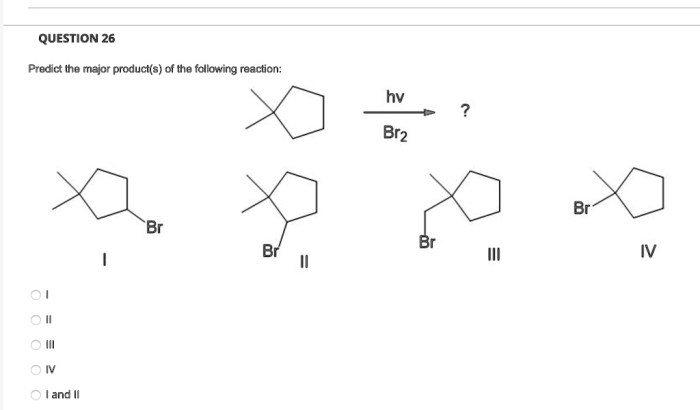
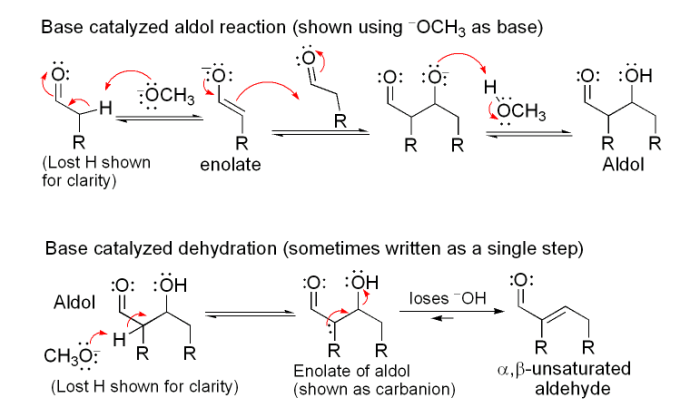
Draw the structure or structures produced by the catalytic reduction – Delving into the realm of catalytic reduction, this comprehensive guide unveils the intricacies of this process, exploring its profound impact on the structural composition of organic compounds. By unraveling the fundamental principles and mechanisms at play, we embark on a journey to decipher the diverse structural transformations induced by catalytic reduction.
Catalytic reduction, a versatile technique employed in various industries, offers a transformative power in chemical synthesis and pharmaceutical production. Through this process, the introduction of hydrogen atoms into organic molecules leads to a myriad of structural alterations, ranging from simple bond saturation to complex rearrangements.
1. Catalytic Reduction
An Overview
Catalytic reduction is a chemical process that involves the addition of hydrogen to a compound in the presence of a catalyst. This process is widely used in various industries, including chemical synthesis, pharmaceutical production, and environmental remediation.
The basic principle of catalytic reduction is that the catalyst facilitates the transfer of hydrogen atoms from a reducing agent to the target compound. This results in the reduction of the target compound, which can lead to changes in its structure, reactivity, and other properties.
2. Structural Effects of Catalytic Reduction
Catalytic reduction can alter the structure of organic compounds in several ways, including:
- Hydrogenation:Addition of hydrogen to a double or triple bond, resulting in the formation of a single bond.
- Deoxygenation:Removal of oxygen atoms from a compound, resulting in the formation of a hydrocarbon.
- Desulfurization:Removal of sulfur atoms from a compound, resulting in the formation of a hydrocarbon.
- Hydrodehalogenation:Removal of halogen atoms from a compound, resulting in the formation of a hydrocarbon.
3. Common Catalytic Reduction Methods
The most commonly used catalytic reduction methods include:
- Hydrogenation:Uses hydrogen gas and a metal catalyst, such as palladium or platinum.
- Catalytic Transfer Hydrogenation:Uses a hydrogen donor, such as isopropanol or formic acid, and a metal catalyst.
- Reductive Amination:Uses ammonia or an amine and a metal catalyst to add hydrogen and nitrogen to a carbonyl group.
- Hydrodesulfurization:Uses hydrogen gas and a metal catalyst to remove sulfur from organic compounds.
4. Applications of Catalytic Reduction
Catalytic reduction is used in a wide range of industries, including:
- Chemical synthesis:Production of pharmaceuticals, fragrances, and other chemicals.
- Pharmaceutical production:Synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients and intermediates.
- Petroleum refining:Removal of sulfur from gasoline and diesel fuel.
- Environmental remediation:Treatment of wastewater and removal of pollutants from air.
5. Factors Affecting Catalytic Reduction, Draw the structure or structures produced by the catalytic reduction
The outcome of catalytic reduction reactions is influenced by several factors, including:
- Catalyst:Type, activity, and selectivity of the catalyst.
- Reaction conditions:Temperature, pressure, and solvent.
- Substrate:Structure and reactivity of the target compound.
- Hydrogen source:Type and availability of hydrogen.
6. Design of Catalytic Reduction Systems
The design of efficient catalytic reduction systems involves considering the following factors:
- Catalyst selection:Choosing the appropriate catalyst based on the target reaction and substrate.
- Reactor design:Optimizing reactor type, size, and configuration for efficient mass and heat transfer.
- Operating conditions:Determining the optimal temperature, pressure, and solvent conditions for the reaction.
Quick FAQs: Draw The Structure Or Structures Produced By The Catalytic Reduction
What is the significance of catalytic reduction in organic chemistry?
Catalytic reduction plays a crucial role in organic chemistry by providing a controlled and efficient means to modify the structure of organic compounds. It enables the selective introduction of hydrogen atoms into molecules, leading to various structural transformations and the synthesis of complex molecules.
How does catalytic reduction alter the structure of organic compounds?
Catalytic reduction can induce a range of structural changes in organic compounds, including the reduction of double and triple bonds, the hydrogenation of aromatic rings, and the cleavage of certain functional groups. These transformations alter the molecular connectivity and hybridization of atoms, leading to the formation of new compounds with distinct properties.
What are the advantages of using catalytic reduction over other reduction methods?
Catalytic reduction offers several advantages over other reduction methods, such as high selectivity, mild reaction conditions, and the ability to use a wide range of substrates. Catalysts enable the reaction to proceed under milder conditions, reducing the risk of side reactions and undesired byproducts.